THM Identity and Access Management
Task 1 - Introduction
In this room, we will cover some concepts which answer to the question “How to verify a legitimate user and how to restrict access ?”.
- Identification
- Authentication
- Strong passwords and Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
- Authorisation and Access Control
- Logging and Auditing
Learning Objectives
By the end of this room, we will gain the knowledge about the following concepts:
- Identification
- Authentication
- Authorisation
- Accountability
- Access Control Models
- Single Sign-On
Task 2 - IAAA Model
IAAA stands for Identification, Authentication, Authorization and Acountability and they are the four pillars of information security.
These four stages consists of :
- Identification is the process of verifying who the user is. It starts with a user claiming an identity, like a username, an email address…
- Authentication is the process of ensuring the user is the one he pretends to be. This can be made through passwords, SSO, one-time codes…
- Authorization determines what rights the user has to access to something. This process is usually done by assinging roles and permissions to an account and normally, the only ones the user needs to perform his actions.
- Accountability tracks the user’s activity to ensure who is responsible for what. This is typically done by logging all the user activity and storing it in a centralized location.
IAAA helps prevent unauthorised access, data breaches, and other security incidents. By implementing these best practices, organisations can protect their sensitive information and resources from internal and external threats.
Questions
You are granted access to read and send an email. What is the name of this process?
Answer: Authorisation
Which process would require you to enter your username?
Answer: Identification
Although you have write access, you should only make changes if necessary for the task. Which process is required to enforce this policy?
Answer: Accountability
Task 3 - Identification
Identification is how the user claims a specific identity without verifying. This is made through a unique number, name, email address…
However, without a proper authentication system, anyone can claim to be anything, like giving a fake identity.
Questions
Which of the following cannot be used for identification?
- Email address
- Mobile number with international code
- Year of birth
- Passport number
Answer: 3
Which of the following cannot be used for identification?
- Landline phone number
- Street number
- Health insurance card number
- Student ID number
Answer: 2
Task 4 - Authentication
Authentication is the process of verifying the user’s identity. Identification and Authentication are core components of any information system and network. It is essential to understand the difference between authentication and identification.
This process is usually accomplished through one of the following ways:
- Something you know: Password, OTP/OTC…
- Something you have: License dongle, card…
- Something you are: Biometrical informations like fingerprint or face recognition.
Two other methods are less used but can also be taken in account:
- Somewhere you are (logical/physical location).
- Something you do (behaviour).
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
MFA refers using two or more of the above mechanisms. The purpose is to add a security in case one of it is compromised like a password getting hacked but using MFA, to access to the account, an authenticator code is needed.
Questions
Answer the following questions using the correct item number from the numbered list below.
- Something you know
- Something you have
- Something you are
- 2FA
When you want to check your email, you enter your username and password. What kind of authentication is your email provider using?
Answer: 1
Your bank lets you finish most of your banking operations using its app. You can log in to your banking app by providing a username and a password and then entering the code received via SMS. What kind of authentication is the banking app using?
Answer: 4
Your new landline phone system at home allows callers to leave you a message when the call is not picked up. You can call your home number and enter a secret number to listen to recorded messages. What kind of authentication is being used here?
Answer: 1
You have just started working at an advanced research centre. You learned that you need to swipe your card and enter a four-digit PIN whenever you want to use the elevator. Under which group does this authentication fall?
Answer: 4
Task 5 - Authorisation and Access Control
Once authenticated, authorization specifies what the user should be allowed to access and do. This means defining permissions and privileges to a user.
Access control on another side, enforces the given policy to ensure only authorized people can access to the given content.
Questions
In the following questions, answer with 1 or 2 to indicate:
- Authorisation
- Access Control
The new policy states that the secretary should be able to send an email on the manager’s behalf. What is this policy dictating?
Answer: 1
You shared a document with your colleague and gave them view permissions so they could read without making changes. What would ensure that your file won’t be modified?
Answer: 2
The hotel management decided that the cleaning staff needed access to all the hotel rooms to do their work. What phase is this decision part of?
Answer: 1
Task 6 - Accountability and Logging
Accountability ensure the users, once authorised to access a system, can be held responsible for their actions. This is possible if there is auditing capabilities, which requires logging.
Logging
Logging is the process of recording events that occur within a system. This process includes user actions, system events, and errors. By logging user actions, an organisation can maintain a record of who accessed what information and when. This record is vital for regulatory compliance, incident response, and forensic investigations.
A comprehensive logging system can identify anomalies and alert or take actions over them if configured for.
Logs should be tamperproof in order to not be deleted, that is why a separate logging server is a good practive in a network.
Log forwarding is the process of sending log data from one system to another. This process often aggregates log data from multiple sources into a central location for more accessible analysis and management.
By centralizing log data, potential security threats can be more easily identified by analysing and correlating collected log events.
Logging and SIEM
Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) is a technology that aggregates log data from multiple sources and analyses it for signs of security threats. SIEM solutions can help organisations identify anomalies, detect potential security incidents, and provide alerts to security teams.
SIEM and logging also provides benefits such as compliance reporting and forensic investigations. Compliance reporting helps meet reporting requirements by collecting data necessary for audits. Forensic investigations are crucial in identifying the source and cause of a security incident and need a detailed system and network activity history.
Task 7 - Identity Management
Identity Management (IdM) includes all the necessary policies and technologies for IAAA. It ensures that only authorised people have access to the needed assets and resources for working properly while unauthorized people are being denied.
IdM helps in the tasks of:
- Protecting sensitive data
- Complying with regulations
- Simplifying user access process
- Improving UX (User Experience)
- Reducing costs
IdM must be implemented correctly with effective strategies to ensure these rules are respected.
Sometimes, IdM and Identity and Access Management (IAM) can be used interchangeably. However, some sources state that IdM tend to be more focus on Authentication and Permissions with users, devices and group management while IAM is more concerned with evaluating attributes and permissions for granting or denying access.
Identity Management (IdM)
IdM is the essential cybersecurity component that refers to the process of managing and controlling digital identities. It involves:
- Authentication
- Authorization
- Access Control
The main goal is to ensure the access of authorized individuals only. They are use to manage user identities across an organization’s network.
IdM systems use a centralized database to store identities and access rights. IdM systems generally include features such as user provisioning, authentication, and authorisation. User provisioning refers to the process of creating and managing user accounts, while authentication and authorisation refer to verifying the identity of a user and granting access to specific resources.
To resume, IdM simplifies the user identity and access management by centralizing it.
Identity and Access Management (IAM)
IAM is like subcategory of IdM. It works with the IdM but it focuses more on identity and access management. It ensures that only authorized users have access to specific resources. It also monitors and controls access.
It is a comprhensive and secure solution to access to resources by providing various technologies like role-based access control, Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) and Single Sign On (SSO).
IAM help organization comply with regulatory requirements such as HIPAA or GDPR. they provide functionalities to manage lifecycle of user identities, including onboarding, offboarding, and access revocation.
To clarify, IdM systems manage user identities, while IAM systems encompass broader functions to manage and secure digital identities and access rights.
Questions
What does IdM stand for?
Answer: Identity Management
What does IAM stand for?
Answer: Identity and Access Management
Task 8 - Attacks Against Authentication
In the real world and even in the digital world, having a passphrase to enter somewhere is almost impossible to be secure without cryptography because it can be known by unwanted people.
Replay Attack
A user log in on a page and the password is encrypted. Unfortuantely, the attacker uses the encrypted version and can login to the account.
Unique Challenge Response
An encrypted password with always the same value is easy to circumvent. One approach would be to send an encryption of the current time along with the password. It requires for both parts to synchronize their clocks and ensures the response is only valid for a brief time.
This is one way to do it and although it is not that secure, authentication protocols are beyond the scope of this room.
Question
The attacker could authenticate using the user’s response when the authentication protocol required a password encrypted with a shared key. What is the name of the attack?
Answer: Replay Attack
Task 9 - Access Control Models
A system controls access to various resources based on the chosen model. Some of the common ones are:
- Discretionary Access Control (DAC)
- Role-Based Access Control (RBAC)
- Mandatory Access Control (MAC)
Discretionary Access Control
DAC is the fact of explicitely giving permissions to users. This is mainly used on sharing plateforms/file access and on a small scale because this process is very straightforward and fully controled by the data owner.
Role-Based Access Control
RBAC uses an intuitive approach of control. Each user has one or more roles, furthermore they are authorized to access different resources based on their roles. Authroization and access will be granted based on the group the user belongs to.
This approach makes maintenance more manageable and efficient by adding or removing roles if needed.
Mandatory Access Control
MAC prioritize security and significantly limit users’ abilities. In other words, users do not need to carry out tasks beyond the strictly necessary like install new software.
SELinux or AppArmor are great exemples of MAC on Linux ditributions.
Questions
Answer the following questions using the correct item number from the numbered list below.
- DAC
- RBAC
- MAC
You are sharing a document via a network share and giving edit permission only to the accounting department. What example of access control is this?
Answer: 2
You published a post on a social media platform and made it only visible to three out of your two hundred friends. What kind of access control did you use?
Answer: 1
Task 10 - Single Sign On
Accessing resources on multiple platforms usally requires multiple login credentials for successful secure authentication. The number of different usernames and passwords makes it quite challenging.
Single Sign On (SSO) tackles this problem beacause it provides a centralized authentication method, which means one login credential to remember.
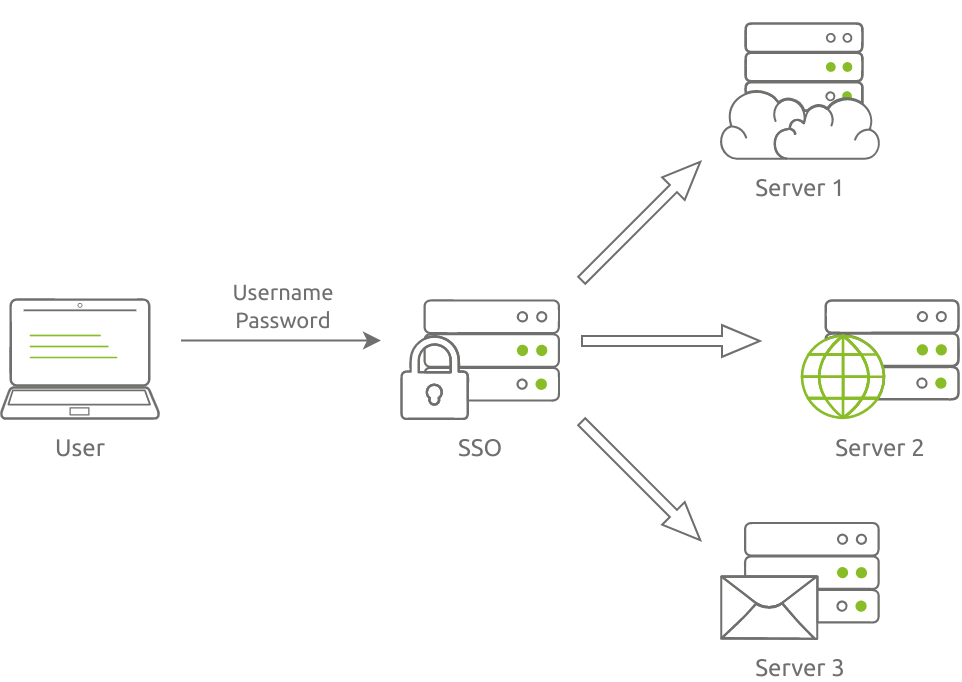
Some advantages are:
- One strong password: One credential to remember.
- Easier MFA: MFA configured once.
- Simpler support: Support requests one one account (e.g: Password reset).
- Efficiency: One time login.
Some disadvantages:
- More dangerous compromising: If the account is compromised, every resources with SSO access are compromised too.
- Outage incident: Every accesses are unavailable without SSO.
- Complexity: SSO implementation and session are complex to make.
Questions
What does SSO stand for?
Answer: Single Sign-On
Does SSO simplify MFA use as it needs to be set up once? (Yea/Nay)
Answer: Yea
Is it true that SSO can be cumbersome as it requires the user to remember and input different passwords for the various services? (Yea/Nay)
Answer: Nay
Does SSO allow users to access various services after signing in once? (Yea/Nay)
Answer: Yea
Does the user need to create and remember a single password when using SSO? (Yea/Nay)
Answer: Yea
Task 11 - Scenarios
Answer the options on the View Site button.
- Fingerprint/Pattern/Code: Authentication
- ATM random code: Identification
- Mail: Id
- Policy: Authorisation
- Name: Id
- Unix logging attempts: Logging
- shadow: Access Control
- Pattern: Auth
answer: {THM_ACCESS_CONTROL}
Task 12 - Conclusion
In this room, we covered the different processes, from identification to logging. We also discussed access control models, SSO, and standards related to authentication and authorisation.
Enjoy Reading This Article?
Here are some more articles you might like to read next: