THM Governance & Regulation
Task 1 - Introduction
In cybersecurity, where malicious actors relentlessly endeavour to exploit vulnerabilities in highly-sensitive systems, we have to combat these threats with a comprehensive approach to information security governance & regulation. Such an approach requires establishing robust policies and guidelines and implementing rigorous monitoring and enforcement mechanisms to ensure compliance
Learning Objectives
- Understanding the role and importance of governance and regulation in cyber security
- Gain an understanding of relevant international laws, regulations, policies, standards & guidelines
- Understanding Governance, Risk Management & Compliance (GRC) framework
- Develop & raise own cyber security posture as per international standards, including ISO 27001, NIST 800-53, and many more
Task 2 - Why is it important?
Important Terminologies
- Governance: Managing and directing an organization/system to achieve its objectives and ensure compliance with laws, regulations, and standards.
- Regulation: A rule/law enforced by a gorvening body to ensure compliance and protect against harm.
- Compliance: The state of adhering to laws/regulations/standards that apply to an organization/system.
Information Security Governance
Information Security Governance represents an organization’s established structure, policies, methods and guidelines designed to guarantee the privacy, reliability and accesibility of its information assets.
To keep away unauthorized intrusion, an ISG should fall under the following processes:
- Strategy: Developing and implementing a comprehensive information security strategy that aligns with the organisation’s overall business objectives.
- Policies and procedures: Preparing policies and procedures that govern the use and protection of information assets.
- Risk management: Conduct risk assessments to identify potential threats to the organisation’s information assets and implement risk mitigation measures.
- Performance measurement: Establishing metrics and key performance indicators (KPIs) to measure the effectiveness of the information security governance program.
- Compliance: Ensuring compliance with relevant regulations and industry best practices.
Information Security Regulation
Information security regulation refers to legal and regulatory frameworks that govern the use and protection of information assets. Regulations are designed to protect sensitive data from unauthorized access, theft, and misuse. GDPR in Europe is one of the many standards available out there.
Key Benefits
- More robust security posture with releveant regulation compliance.
- Increased stakeholder confidence by proving implemented measures.
- Regulatory compliance to avoid legal and financial penalties.
- Better alignment with business objectives to ensure cost-effective security measures.
- Informed decision-making to se where security measures are the most needed.
- Competitive advantage by enhancing stakeholders trust.
Relevant Laws and Regulations
| Law/Regulation | Domain | Description |
|---|---|---|
| General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) | Data Privacy & Protection | GDPR is a regulation propagated by the European Union that sets strict requirements for how organisations handle and protect and secure the personal data of EU citizens and residents. |
| Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) | Healthcare | A US-based official law to maintain the sensitivity of health-related information of citizens. |
| Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI-DSS) | Financial | Set technical and operational requirements to ensure the secure handling, storage, processing, and transmission of cardholder data by merchants, service providers, and other entities that handle payment cards. |
| Gramm-Leach-Bliley Act (GLBA) | Financial | Financial companies must be sensitive to their customers’ nonpublic personal information (NPI), including implementing information security programs, providing privacy notices, and disclosing information-sharing practices. |
Questions
The term used for legal and regulatory frameworks that govern the use and protection of information assets is called?
Answer: Regulation
Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) targets which domain for data protection?
Answer: Healthcare
Task 3 - Information Security Frameworks
ISF provides a set of documents that outline the organisation’s approach to information security and governs how security is implemented, managed, and enforced within the organisation. This mainly includes:
- Policies: A formal statement that outlines an organisation’s goals, principles, and guidelines for achieving specific objectives.
- Standards: A document establishing specific requirements or specifications for a particular process, product, or service.
- Guidelines: A document that provides recommendations and best practices (non-mandatory) for achieving specific goals or objectives.
- Procedures: Set of specific steps for undertaking a particular task or process.
- Baselines: A set of minimum security standards or requirements that an organisation or system must meet.
Developing Governance Documents
- Identify the scope and purpose of the document.
- Research and review relevant laws, regulations, industry standards, and best practice.
- Draft the document by writing clear and concise.
- Review and approval by experts.
- Implementation and communication to all relevent employees and stakeholders.
- Review and update periodically to stay up-to-date.
Questions
The step that involves periodic evaluation of policies and making changes as per stakeholder’s input is called?
Answer: Review and Update
A set of specific steps for undertaking a particular task or process is called?
Answer: Procedures
Task 4 - Governance Risk and Compliance (GRC)
GRC focuses on steering the organisation’s overall governance, enterprise risk management, and compliance in an integrated manner. It helps to ensure the organization operates within relevant regulations and industry standards. It has three components:
- Governance: Rules, processes and policies to steer the organization.
- Risk Management: Day-to-day technical processes to mitigate the risk.
- Compliance: Ensurements to meet standards and run legally.
How to Develop GRC Program
- Define the scope and objectives for a branch or a company.
- Conduct a risk assessment by identifying the cyber risks.
- Develop policies and procedures to guide to the best practicies.
- Establish governance processes to ensure the GRC program is effecively managed and controlled.
- Implement controls and operations to mitigate risks identified in step 2.
- Monitor and measure performance to ensure the effectiveness of the program.
- Continuously improve the program.
Questions
What is the component in the GRC framework involved in identifying, assessing, and prioritising risks to the organisation?
Answer: Risk management
Is it important to monitor and measure the performance of a developed policy? (yea/nay)
Answer: yea
Task 5 - Privacy and Data Protection
In every sector, privacy and data protection regulations are critical as they deal with citizens’ Personally Identifiable Information (PII). Privacy regulations help ensure PII is handled and stored responsibly and ethically to establish trust between clients and actors.
General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR)
GDPR is a data protection law implemented in 2018 in the EU. It applies to all business entities that conducts business in the EU and collect/stor/process data of EU residents. Companies can only collect personal data for a legitimate reason and must inform the owner about its processing. The three key points are:
- Prior approval must be obtained before collecting any personal data.
- Personal data should be kept to a minimum and only collected when necessary.
- Adequate measures are to be adopted to protect stored personal data.
If these are not respected, penalties and fines could be charged against the company:
- Tier 1: Unintended data collection, sharing data with third parties without consent, etc. Maximum penalty amounting to 4% of the organisation’s revenue or 20 million euros.
- Tier 2: Data breach notifications, cyber policies, etc. The maximum fine for Tier 2 is 2% of the organisation’s revenue or 10 million euros.
Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS)
PCI DSS is focused on maintaining secure card transactions and protecting against data theft and fraud. It requires strict control access to cardholder information and monitoring unauthorised access, using recommended measures such as web application firewalls and encryption. Online card-based transactions are the main target for this regulatory.
Questions
What is the maximum fine for Tier 1 users as per GDPR (in terms of percentage)?
Answer: 4
In terms of PCI DSS, what does CHD stand for?
Answer: CHD
Task 6 - NIST Special Publications
NIST 800-53
NIST 800-53 is a publication titled “Security and Privacy Controls for Information Systems and Organisations” developed by the National Institute of Standards and Technology. It serves as a framework for organizations to assess and enhance the security and privacy of their information systems and comply with various laws, regulations, and policies.
NIST 800-53 Revision 5 organises security controls into twenty families, each addressing a specific security concern category.
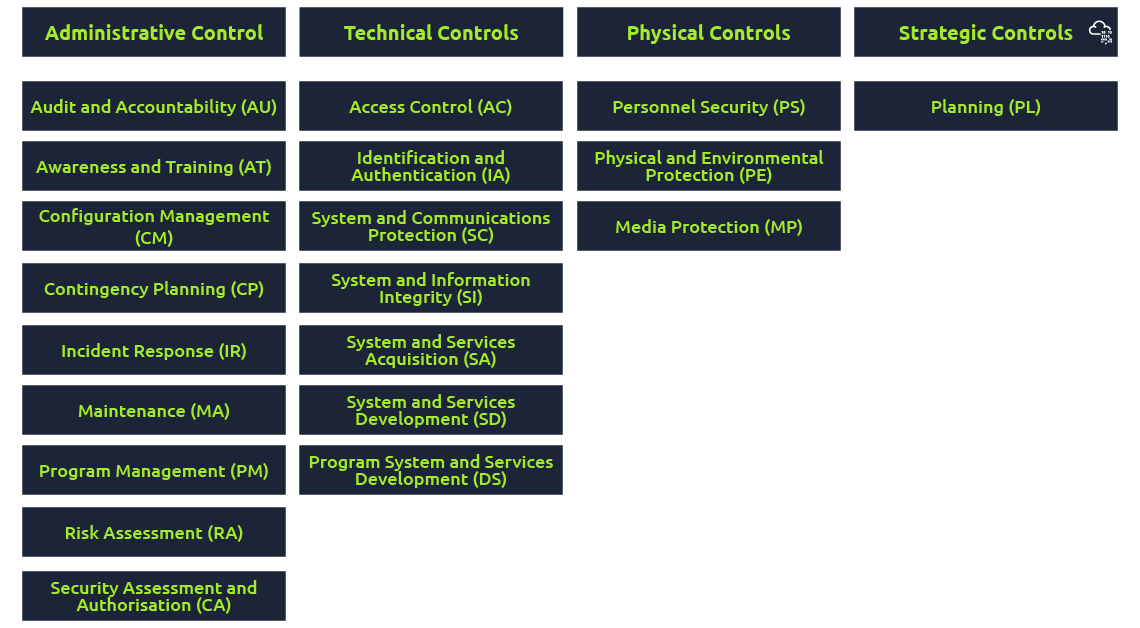
Implmenting NIST 800-53
Program Management is one of the most crucial point of the framework. It dictates establishing, implementing, and monitoring organisation-wide programs for information security and privacy while safeguarding the processed, stored, or transmitted through systems. These subcontrols need to be implmented:
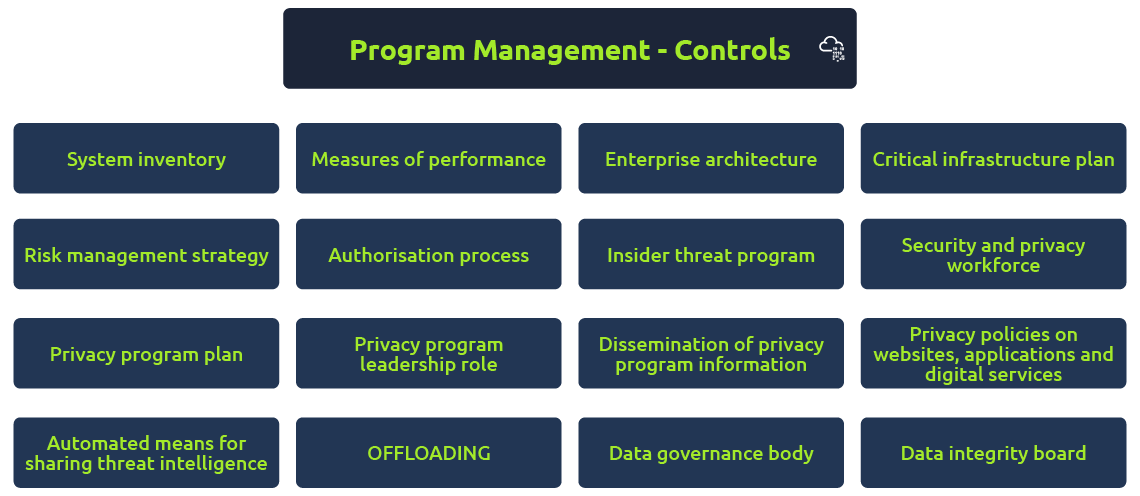
Compliance Best Practices
In order to comply to the best practices, businesses must follow these steps:
- Discover and classify data assets, information systems, and associated threats.
- Map these into the various NIST 800-53 families to create a structured approach for matching the organization’s demands easier.
- Manage governance structure by allocating duties to each family and outline them using access control
- Monitor data activity and user behaviour regularly and avaluate to ensure compliance.
NIST 800-63B
This special publication sets guidelines to help establish effective digital identity practices. It focuses on verifying indentities of individuals and giving levels of identity assurance. It offers adivces on using authentication factors, including passwords, biometrics, and tokens, and securely managing and storing user credentials.
Questions
Per NIST 800-53, in which control category does the media protection lie?
Answer: Physical
Per NIST 800-53, in which control category does the incident response lie?
Answer: Administrative
Which phase (name) of NIST 800-53 compliance best practices results in correlating identified assets and permissions?
Answer: Map
Task 7 - Information Security Management and Compliance
Information Security (IS) management is the panning, execution and continuous administration of security measures. It protects information from unauthorized access, use, disclosure, interruption, alteration, and destruction. To achieve that, it involves risk assessment and identification, security controls and procedures development, incident response planning, and security awareness training.
Compliance refers to observing information security-related legal, regulatory, contractual, and industry-specific standards.
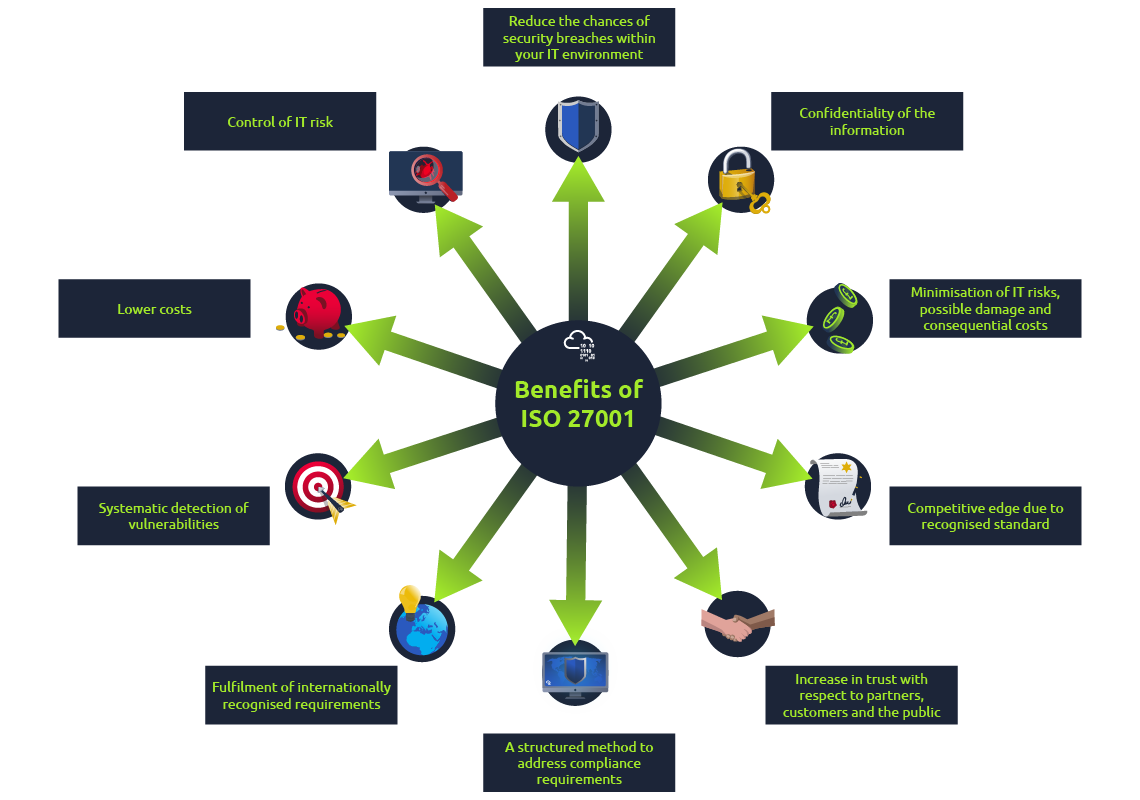
ISO/IEC 27001
ISO 27001 is a standard for requirements to plan, develop, run, and update an organisation’s Information Security Management System (ISMS).
It has the following core component:
- Scope
- Information security policy
- Risk assessment
- Risk treatment
- Statement of Applicability for controls
- Internal audit
- Management review
Service Organisation Control 2 (SOC 2)
SOC2 was developed by the American Institute of Certified Public Accountants (AICPA) as a compliance/auditing framework. It focuses on data security based on CIA triad.
This framework is essential for service providers interacting with client data or offering solutions that process, store, or transmit sensitive data. The primary purpose of the SOC 2 audit is to ensure that third-party service providers store and process sensitive information securely.
Here are the main points on what the audit will be conducted:
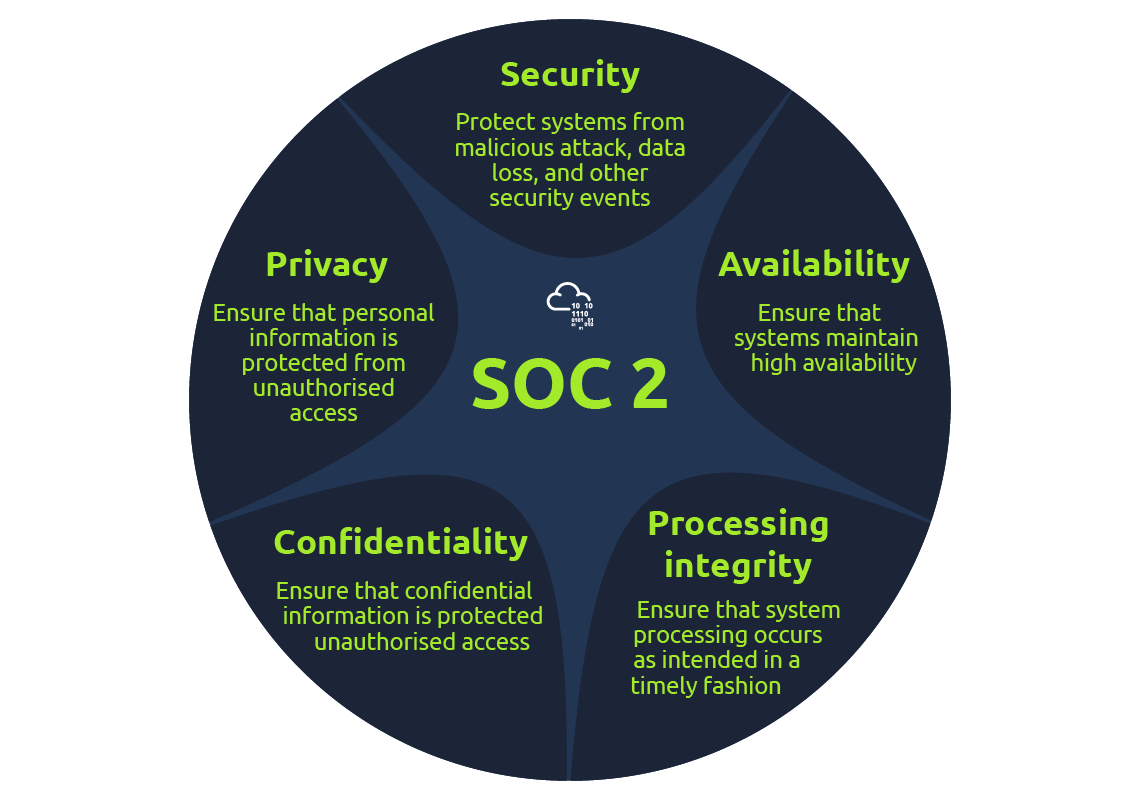
Technical and specific controls, like ensuring data encryption in transit, network security, incident management, etc… can also be reviewed.
Questions
Which ISO/IEC 27001 component involves selecting and implementing controls to reduce the identified risks to an acceptable level?
Answer: Risk Treatment
In SOC 2 generic controls, which control shows that the system remains available?
Answer: Availability
Task 8 - Conclusion
Here, we have seen a comprehensive overview of the importance of developing an effective information security governance and regulation framework to protect an organisation’s valuable assets and sensitive information. We also have viewed laws and regulations about privacy and data protection such as GDPR and PCI DSS. The GRC framework concept has been explained in order to develop a secure organization’s outlook.
Furthermore, we have highlighted different governance enablers, such as ISO/IEC 27001, NIST 800-53, and NIST Special Publication 800-63B, and explained how they provide information security protection to an organisation.
Questions
Click the View Site button at the top of the task to launch the static site in split view. What is the flag after completing the exercise?
Answers: NIST800-53 and SOC2.
Answer: THM{SECURE_1001}
Enjoy Reading This Article?
Here are some more articles you might like to read next: