THM CTF MalBuster
Task 1 - Introduction
In this room, we’ll be charged of analyzing malware samples provided by the SOC Team. We will mainly use FLARE VM (sometimes REMnux) and our knowledge learned in Dissecting PE Headers and Basic Static Analysis.
Task 2 - Challenge Questions
Malware samples are located in Desktop\Samples.
Based on the ARCHITECTURE of the binary, is malbuster_1 a 32-bit or a 64-bit application? (32-bit/64-bit)
To retrieve this information, we will use pestudio to investigate into PE Headers. On FLARE VM, pestudio is available into Desktop\FLARE\Utilities.
When we open this file with the utility, we are directly welcomed with interesting information, including the CPU architecture of the application.
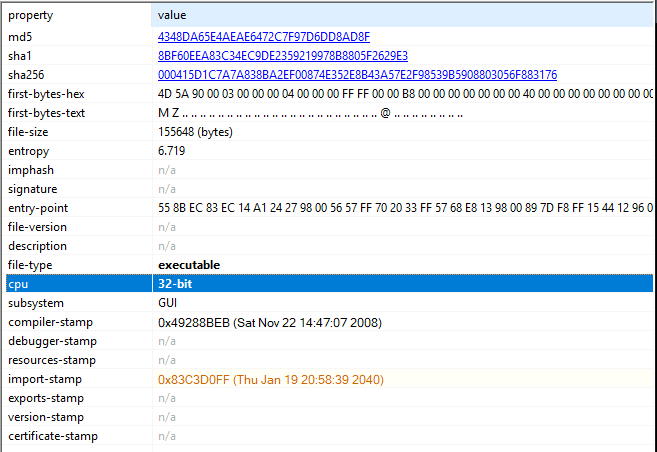
Answer: 32-bit
What is the MD5 hash of malbuster_1?
Using the same tab, we are able to know the md5 of the file.
Answer: 4348DA65E4AEAE6472C7F97D6DD8AD8F
Using the hash, what is the number of detections of malbuster_1 in VirusTotal?
Using the provided md5 hash on virustotal, we are able to see that malware is a trojan.zbot/razy.
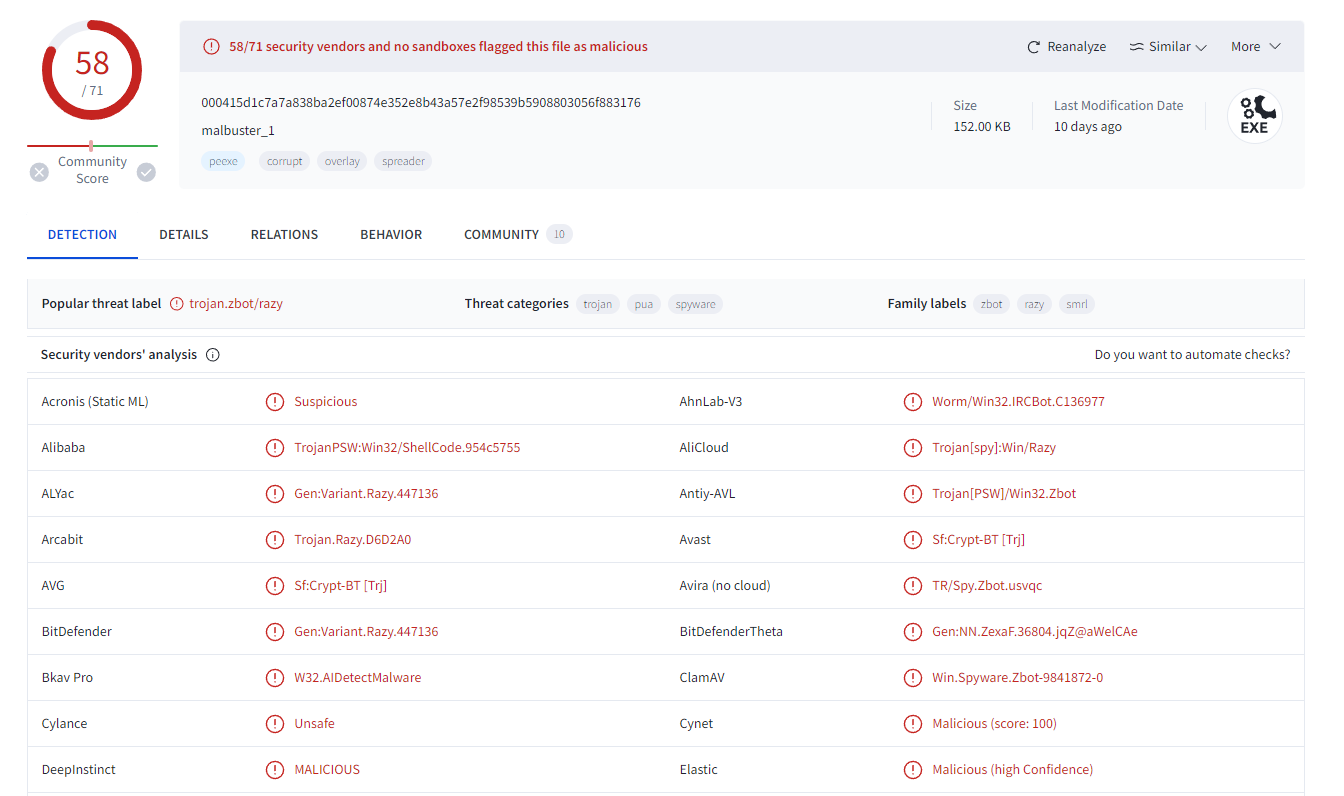
Answer: 58
Based on VirusTotal detection, what is the malware signature of malbuster_2 according to Avira?
To obtain the Avira’s malware signature, we have to go through the same steps as before.
The md5 hash provided by pestudio is 1D7EBED1BAECE67A31CE0A17A0320CB2.
By putting this value on Virustotal, we obtain the following results:
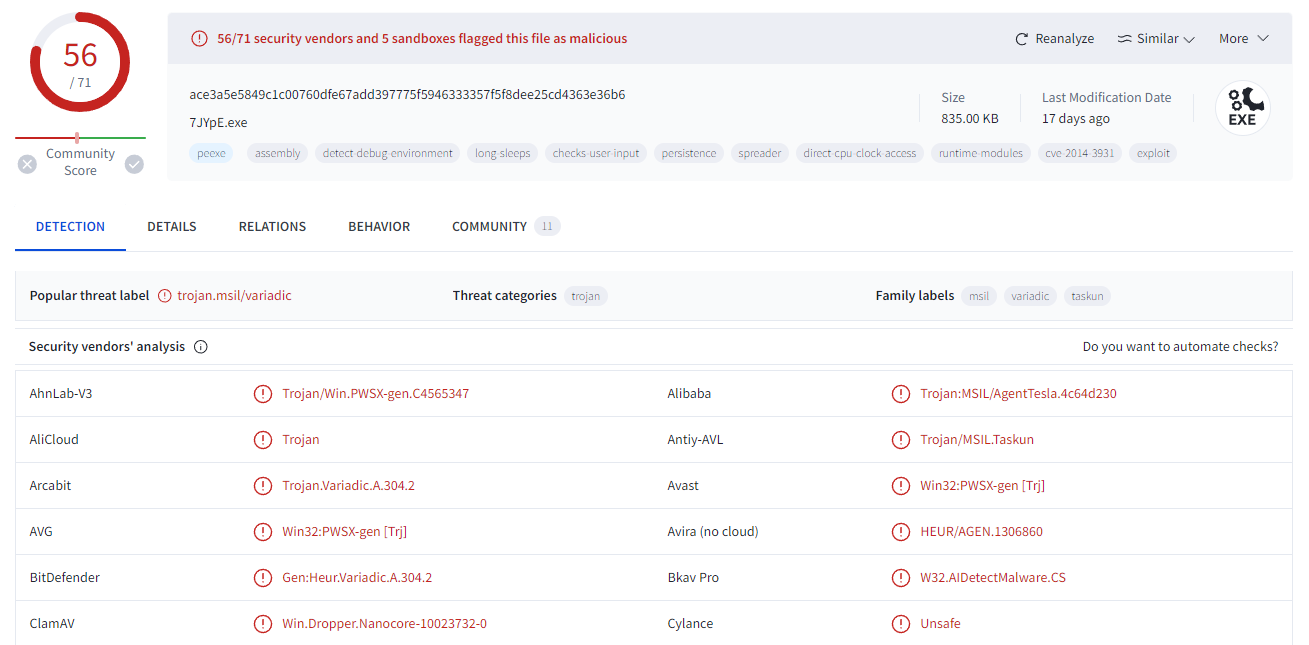
Answer: HEUR/AGEN.1306860
malbuster_2 imports the function _CorExeMain. From which DLL file does it import this function?
According to pestudio, we can see that function comes from .NET Runtime Execution Engine.
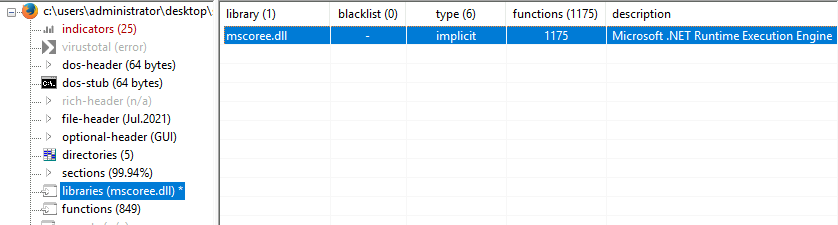
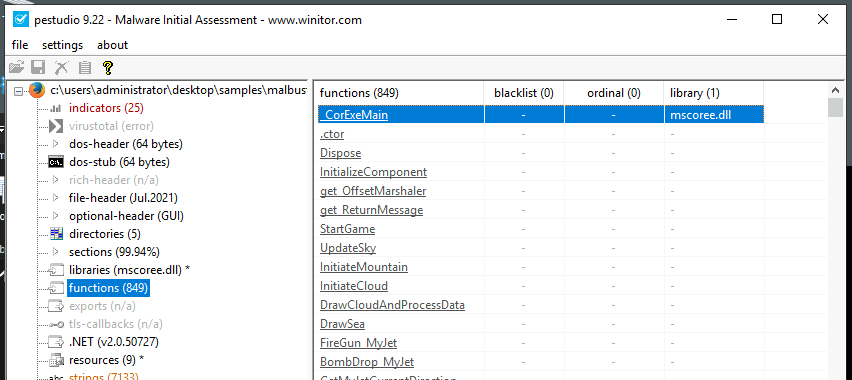
Answer: mscoree.dll
Based on the VS_VERSION_INFO header, what is the original name of malbuster_2?
On pestudio, we can find this header in the version tab.
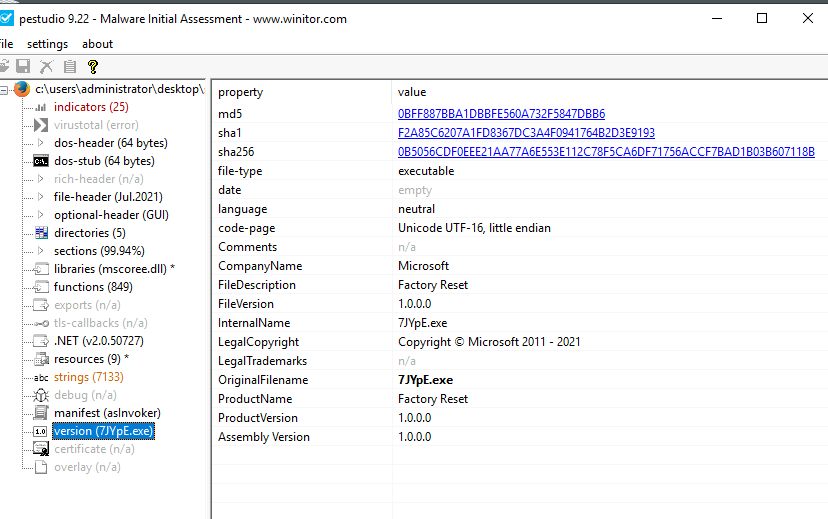
Answer: 7JYpE.exe
Using the hash of malbuster_3, what is its malware signature based on abuse.ch?
We retrieve the executable’s md5 hash on pestudio and then we copy it into abuse.ch.
This is what we get in return:
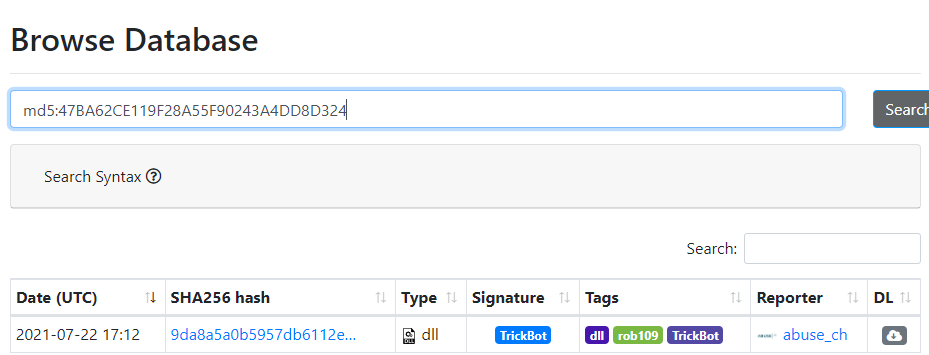
Answer: Trickbot
Using the hash of malbuster_4, what is its malware signature based on abuse.ch?
By doing the same steps, this is what we get from abuse.ch:
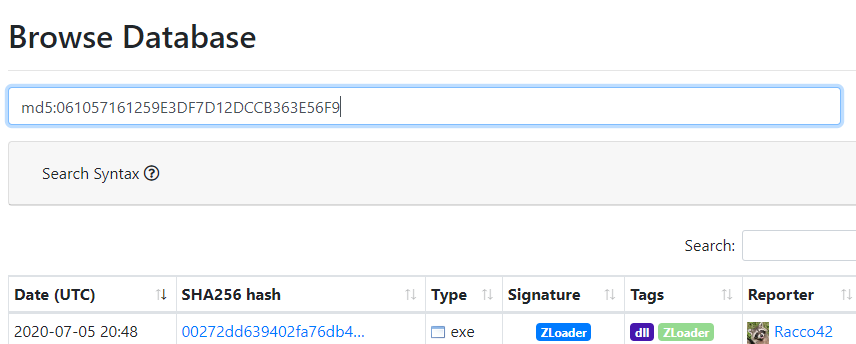
Answer: ZLoader
What is the message found in the DOS_STUB of malbuster_4?
By searching in the DOS Stub, we find that the message is a bit different than usual:
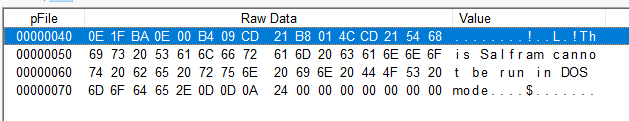
*Answer: This Salfram cannot be run in DOS mode
malbuster_4 imports the function ShellExecuteA. From which DLL file does it import this function?
We can retrieve the imported dlls and functions in the Imports tab in pe-bear. (pestudio could not work)
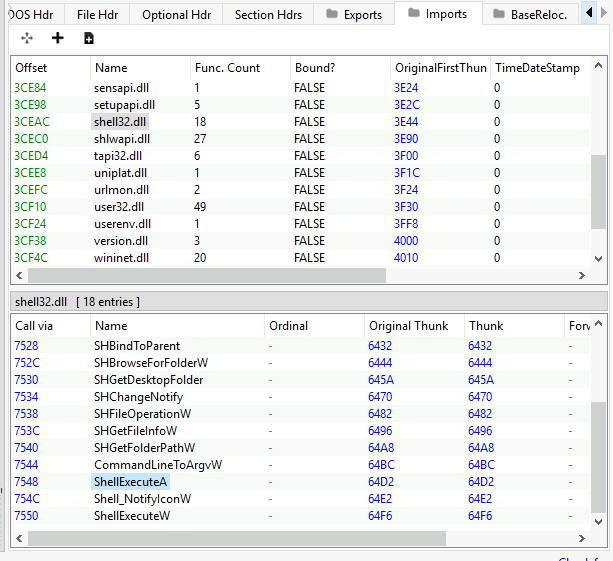
Answer: shell32.dll
Using capa, how many anti-VM instructions were identified in malbuster_1?
Using capa Samples/malbuster_1:
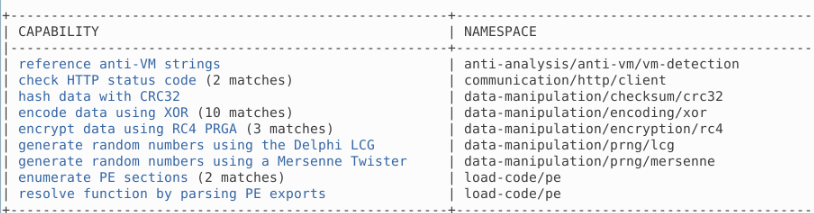
Capa was not able to retrieve how many anti-VM instructions.
Answer: 3
Using capa, which binary can log keystrokes?
After testing each sample, this is what we get on malbuster_3:
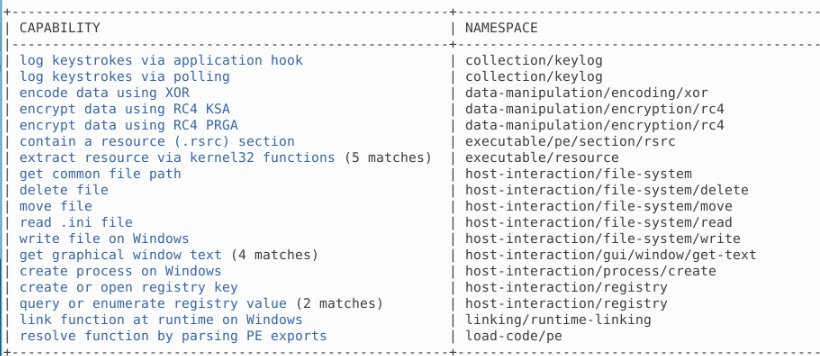
Answer: malbuster_3
Using capa, what is the MITRE ID of the DISCOVERY technique used by malbuster_4?
This is what we get after using capa on the malbuster_4 sample:
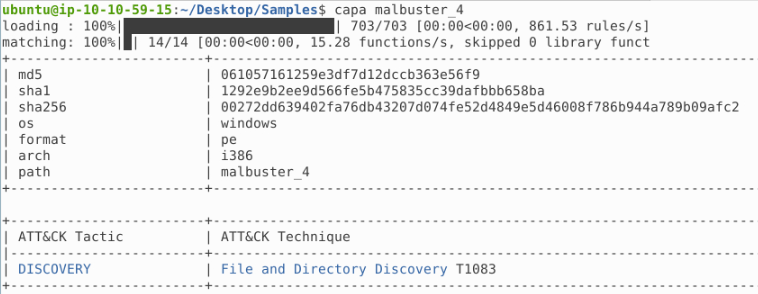
Answer: T1083
Which binary contains the string GodMode?
By testing each sample with strings -f malbuster_* | grep GodMode, we can retrieve in which binary this string is present:
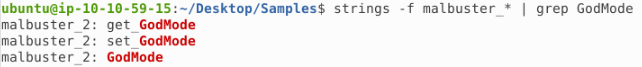
Answer: malbuster_2
Which binary contains the string Mozilla/4.0 (compatible; MSIE 6.0; Windows NT 5.1; SV1)?
We use the same process as before but here we use Mozilla as the keyword.

Answer: malbuster_1
Enjoy Reading This Article?
Here are some more articles you might like to read next: